diagnose esophageal cancer the first series of tests involve examination of the esophagus through images. One such approach requires the doctor to feed a slim, versatile pipe containing a camera through the throat to inspect the esophagus. It may also be necessary to take a small tissue sample in the course of the procedure for subsequent laboratory examination.
Barium Swallow Study
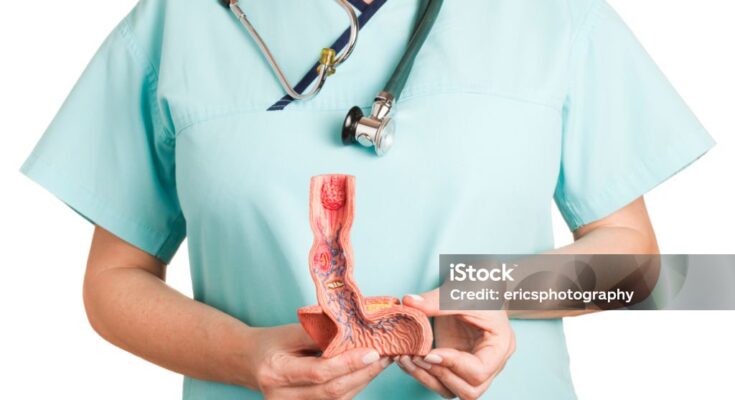
A barium swallow study is an investigative procedure that uses X-rays in order to diagnose problems with the digestive tract. This test can point out defects in the esophagus, including possible tumor. Before the actual procedure, you will be required to take a thick white substance called barium, which forms a coat over the esophagus thus aid in imaging on X-ray. If any signs that cause concern are identified during this study, your doctor may refer you to an endoscopy to get more information.
Upper Endoscopy
is an endoscopic procedure which is performed to inspect the upper part of gastrointestinal tract. This is done with a long, flexible tube called/endoscope which contains a camera at the business end. The endoscope is then passed through the throat into the esophagus in order to investigate for cancer or other complications.
Biopsy
A biopsy is commonly known as removal of tissue from the body and sending it for testing. In this process, a healthcare professionals employs specific sharp tools inserted into an endoscope to capture a small amount of tissue from the esophagus. This sample is then taken to a laboratory to see if there are any sign of cancerous cells.
Assessing Cancer Spread
Additional tests may be done after the Esophageal Cancer diagnosis is given to find out whether the Cancer has spread anywhere else. These are useful in ascertaining the cancer stage; the extent of the disease is referred to as stage. Staging normally involves imaging tests to determine whether there is cancer in the lymph nodes or any other part of the body. It is therefore important to know the results of these tests since your health care team will use the results to plan your treatment.
Other imaging techniques that can be used are bronchoscopy, endoscopic ultrasound, computerized axial tomography (CT), Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET). It i
Cancer staging of the esophagus is in the following manner: Stage 0, Stage I, Stage II, Stage III and IV.
Stage 0 means the cancer is small, at the beginning state and localized at the inner lining of the esophagus. The phases are the stages where the cancer develops in size and gets deeper tissues therefore they move from one another. Stage 4 mean mean that cancer cells have spread to other areas around the esophagus or in the body to the lymph nodes.
Esophageal Cancer treatment
Treatment Options
1. Surgery
Esophageal surgery usually assumes a central role in the management of the localized esophageal cancer. The most common surgical procedures include:
Esophagectomy: This include the surgical resection of part or the total esophagus. The other sections are then sutured to the stomach or throat as the case may be, then the patient is discharged.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): It is recommended in very early stages of cancer and can be performed with the help of an endoscopic removal of the malignant tissue.
Surgery is usually recommended if the cancer is confined to the esophagus and adjacent lymph nodes.
2. Radiation Therapy
Chemotherapy utilizes rays of energy to eliminate the fast growing cancerous cells. It can be used in several contexts: Adjuvant Therapy: Following surgery, radiation can be used to treat residual tumour cells that may be in the body. Neoadjuvant Therapy: In some cases, a cancerous tumor might be treated by radiation ahead of surgery to help with the surgery process by making the tumors smaller. Palliative Treatment: Such patients may get relief through radiation to alleviate symptoms such as pain and dysphagia in advance stages. Innovations in strategies, for instance, IMRT has enhanced the goal and accuracy of radiance therapies.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a process in which chemicals, or drugs, are used to kill cancer cells. They can be used along with surgery and radiation therapy, that is, when the tumor is large and extends to other parts of the body. Common approaches include:
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Administered prior to surgery in an attempt to shrink the tumor.
Adjuvant Chemotherapy: That is given after surgery in order to avoid the chance of recurrence.
Palliative Chemotherapy: It was prescribed to treat symptoms and to increase life expectancy in cases of the final stages of the disease.
Treatment regimens have staggered administration of drugs in the course of the day and frequently use a combination of drugs in a bid to enhance effectiveness while at the same time reducing the growth of resistance.
4 . Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is developed with a mission to eliminate certain aspects of a cancerous cell. For esophageal cancer, medications based on the proposed receptors such as HER2 or drivers of angiogenesis have been most effective. Targeted therapies may also be combined with chemotherapy and radiation although individually.
5 . immunotherapy
One of the revolutionary treatment methods is immunotherapy because it uses the individual’s immune system to combat cancer. It has been increasingly used in the past few years for managing esophageal cancer and more so among patients with advanced diseases. Some agents, like immune checkpoint inhibitors (such as pembrolizumab), have been helpful to some patients who had a few of the options left.
6 . Clinical Trials
Clinical trials: Some esophageal cancer patients perhaps would like to take part in a trial of new treatments and therapies. It must be appreciated that most of these trials afford patients a chance to get the newest type of treatment and in the process enable the development of cancer management.
Conclusion
Esophageal cancer management is complex, and a specific approach depends on the specific case of the patient. Accordingly, a team of surgeon, medical oncologist, radiation oncologist and other health care professionals is recommended.
Esophageal cancer is a difficult diagnosis, but knowing that progress continues to be made in the research and treatment of the disease, should be comforting. It is therefore important that one get diagnosed early, receive thorough treatment plans and be supported by his or her physician. As with any type of cancer, consultation with a competent healthcare provider is advised if you or a family member is diagnosed with esophageal cancer to consider the best way to proceed.
I’m so in love with this. You did a great job!!
Thanks 😊